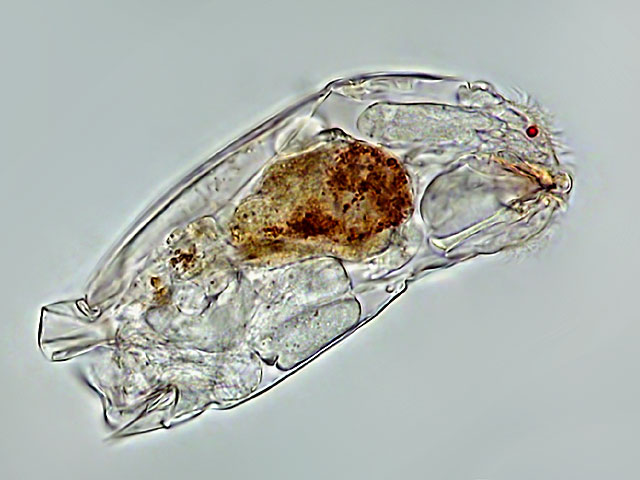
| Cephalodella catellina, lateral view, showing the very short toes and the characteristic fold on the back. (3) |
| |
 |
| Cephalodella catellina, another specimen from (1), lateral view, showing the appendage of the tail above the foot. |
| |
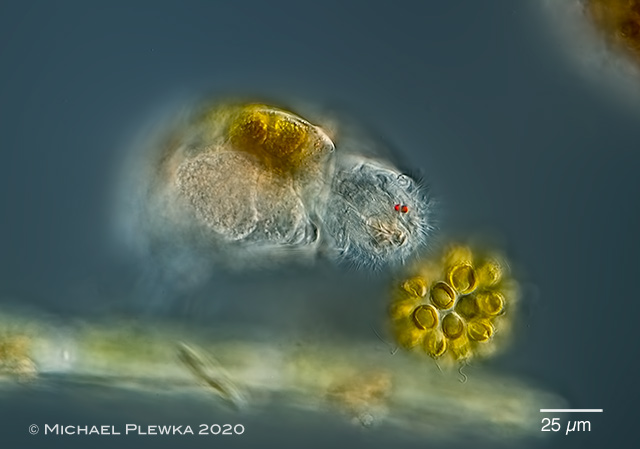 |
| Cephalodella catellina, specimen from (7); feeding on Synura uvella; front view showing the two eyespots. |
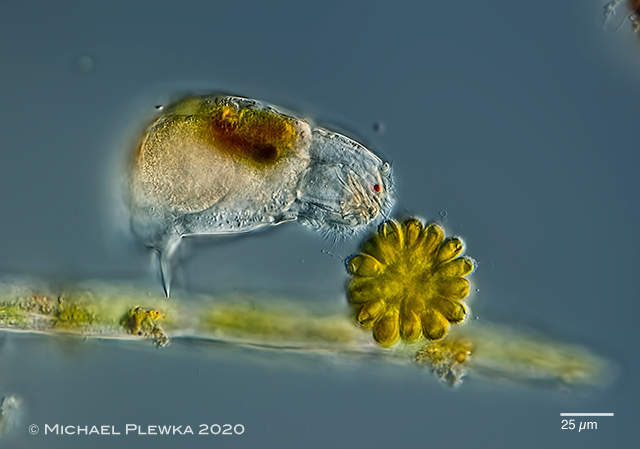 |
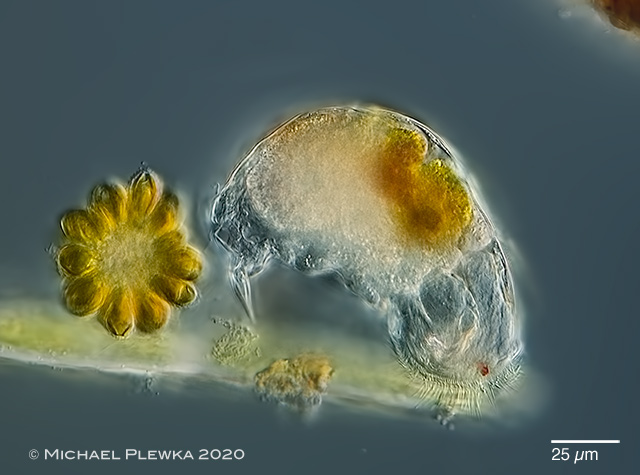
| Cephalodella catellina, same specimen lateral view. |
| |
 |
| Cephalodella catellina, may also feed on bacteria growing on a desintegrating alga. (7) |
| |
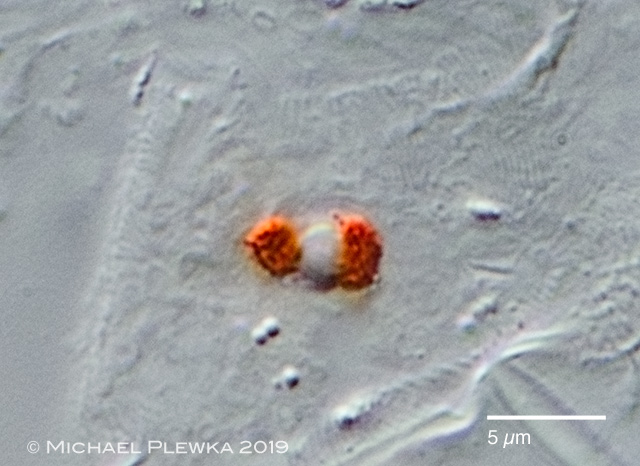 |
| Cephalodella catellina, specimen compressed by coverslide; two eyespots and a common, single lens; detail |
| |
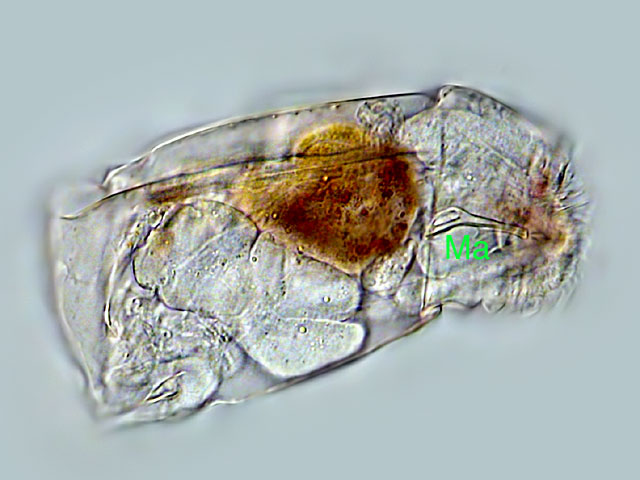 |
| Cephalodella catellina, the manubrium (Ma) features a loop which is closed in contrast to C. catellina major. (2) |
| |
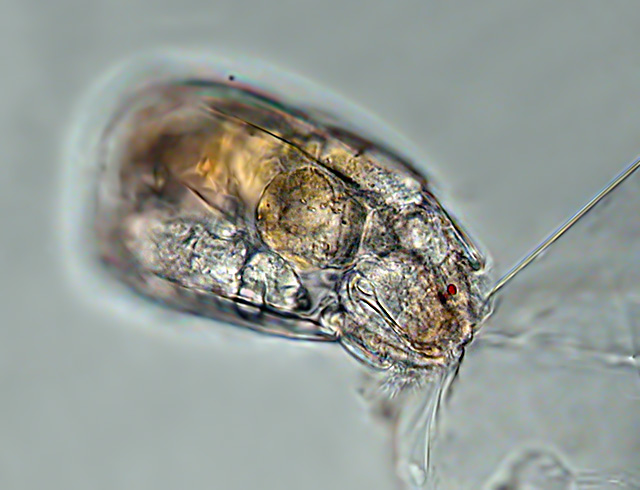 |
| While the predatory rotifer Asplanchna normally feeds on smaller rotifers in this case it is vice versa: the bigger Asplanchna is trapped under the cover slide and cannot escape, while the smaller Cephadelodella can still move and picks the integument of Asplanchna, but is not capable of destroying the tough tissue. (2) |
| |
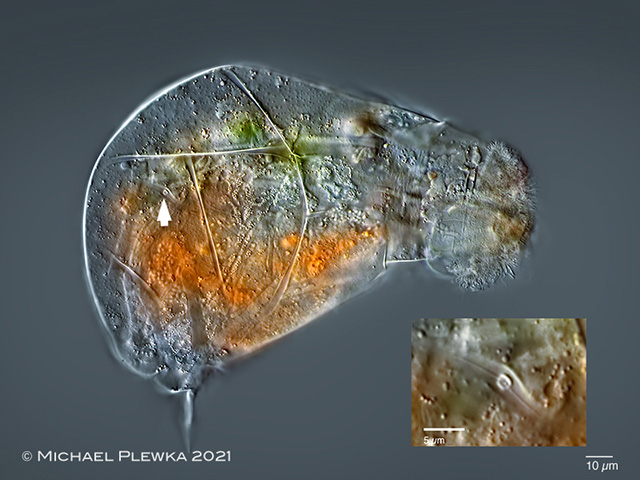 |
| Cephalodella catellina, slightly compressed specimen; the arrowhead points to the (opening of the lateral) antenna, which can be seen in detail in the inset (8) |
| |
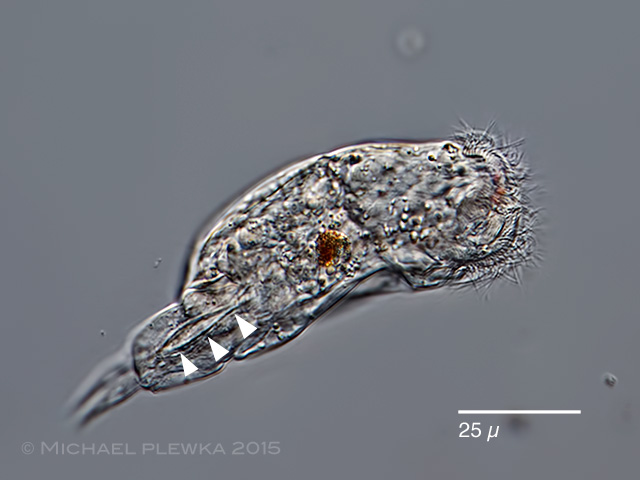 |
| Cephalodella catellina, male specimen, lateral view. The arrowheads point to the copulation organ. (4) |
| |
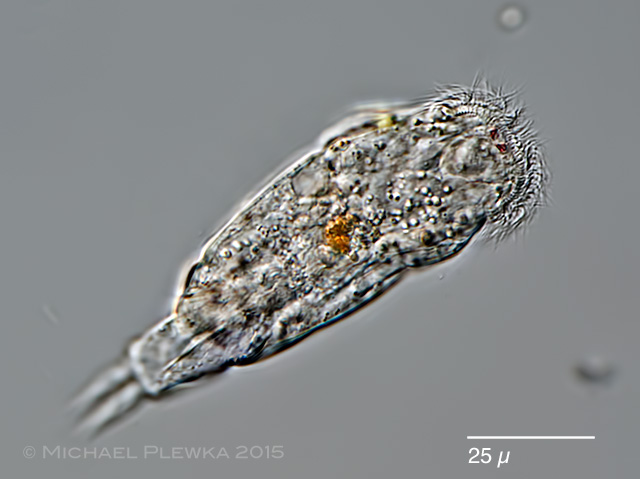 |
| Cephalodella catellina, male specimen, dorsoventral view. (4) |
| |
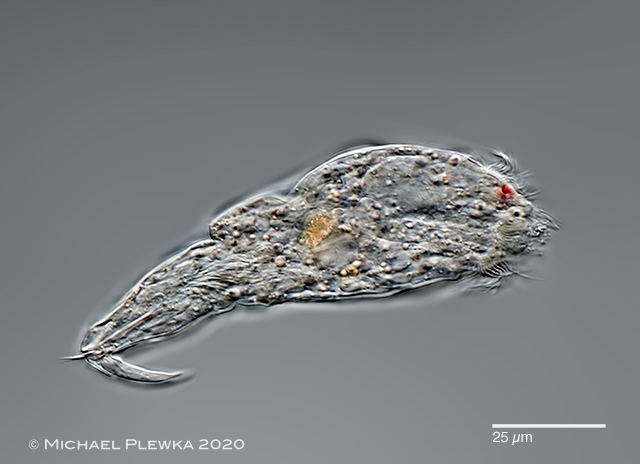 |
| Cephalodella catellina, another male specimen, lateral view. (7) |
| |
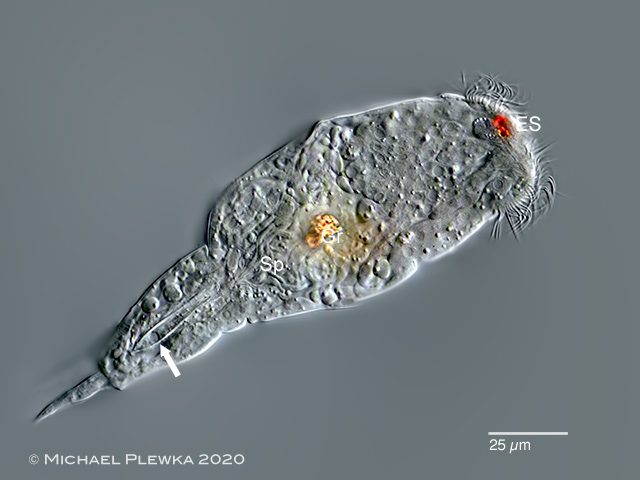 |
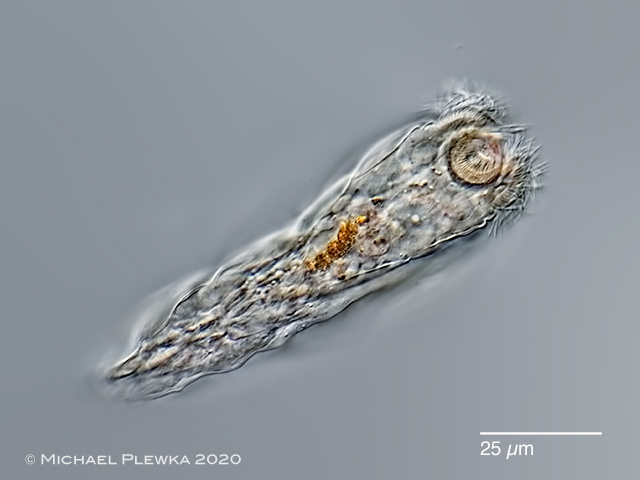
| Cephalodella catellina, male specimen, slightly compressed by coverslide, dorsoventral view; showing the frontal double eyespot (ES). The arrow points to the copulation organ. Gr: light refracting granules; Sp: spern cells. (7) |
| |
 |
| Cephalodella catellina, male specimen, ventral view. There is a conspicous arrangement of the "oral" cilia (7) |
| |
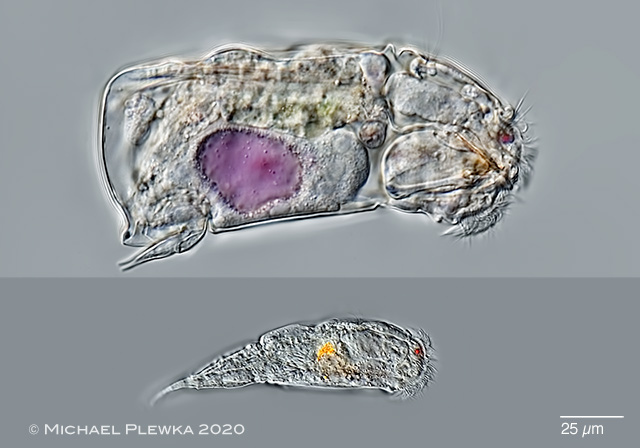 |
| Cephalodella catellina, size comparison between female (upper specimen, the bladder of which is purple colored because of a diet with special cryptophyte alge; see also Cephalodella tenuior) and dwarf male. |
| |
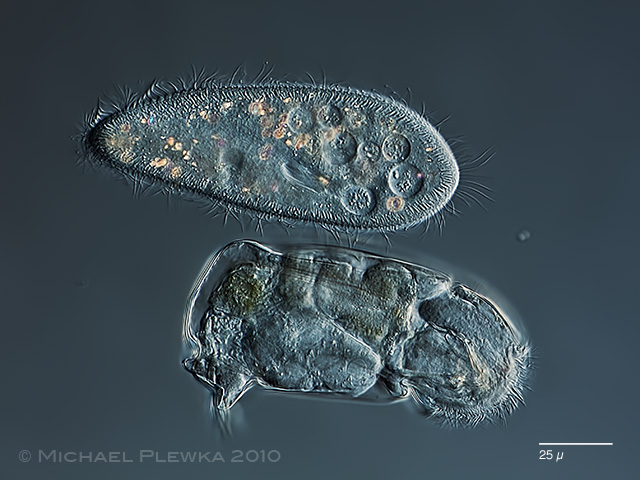 |
| Cephalodella catellina, another size comparison: specimen from (1) together with Paramecium caudatum. (12/2010). While both organisms are about the same size Paramecium accomplishes all vital functions in a single cell. The rotifer Cephalodella has about 1000 cells, which therefore are much smaller than in Paramecium and are partly fused into a syncytium. |
| |
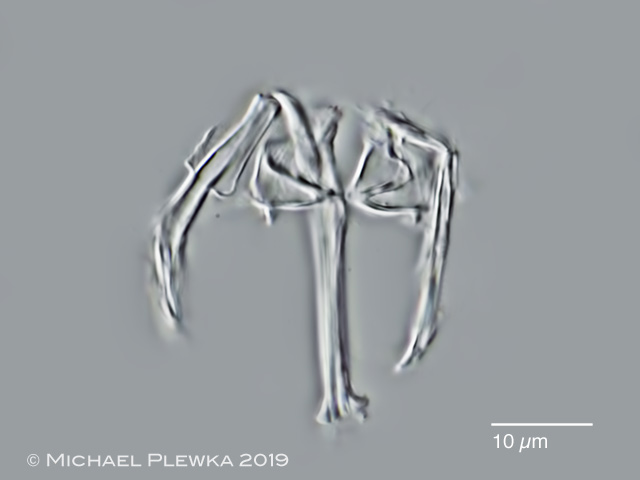 |
| Cephalodella catellina, virgate trophi, type C |
| |
 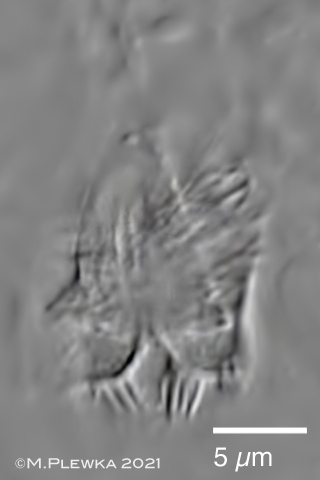 |
| Cephalodella catellina; left image: while macerating for trophi preparation some chitinous fork-like structures of the mouth become visible. right image: detail of the structures. (8) |
| |
| |
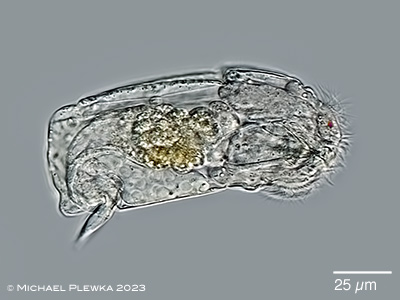 |
| Cephalodella catellina; specimen from (9) |
| |
| Another variety of C. catellina is C. catellina volvocicola |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
 |
| Location (9): nature reserve NSG Unteres Odertal; BB, Germany; Eisvogelbrücke |
| |
| Habitat (9): "aufwuchs" on artificially exposed microslides |
| |
| Date (9): 15.05.2023 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
 |
| Location (6); (7): Felderbachtal, Hattingen, Haselbecke, Teich |
| |
| Habitat (6); (7): Neuston, together with Cephalodella hoodi |
| |
| Date(6); (7) : 24.04.2020 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Location: Gevelsberg, Stefansbachtal, Grünes Klassenzimmer, pond (1;2); "De Gote Put", Antwerp, Belgium (4); Wodantal, Hattingen, Teich (5); Gevelsberg, NRW, Germany, Bruchmühle; pond (8) |
| Habitat: Periphyton/ Detritus (1;2); Periphyton (4); Plankton (5); Neuston, together with Cephalodella hoodi (6,7); detritus (8) |
| Date: 18.03.2006 (1); 13.08.2006 (2); 14.12.2010 (3) 24.02.2015 (4); 02.03.2019 (5); 02-05.2021 (8) |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|